python今年9月份将被国家纳入计算机二级资格证 先学就是鼻祖 几年后你就是大牛
这里可能更新不及时
Python人工智能从入门到精通(黑客入门语言)(持续更新中...) 全部课程 原文地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/ParisGabriel/tag/Python/
Python人工智能从入门到精通 基础篇
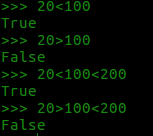
比较运算符:
< 小于
<= 小于等于
> 大于
>= 大于等于
== 等于
!= 不等于 语法: 表达式1>表达式2 返回布尔类型
 数值对象的构造函数: float(obj) 用字符串或数字转换为浮点数,如果不给出实参,则返回0.0 int(x=0,base=10) 用数字或者字符串转换为整数,如果不给出实参,则返回0.0 bas表示是进制 complex(r=0.0,i=0.0) 用数字创建一个复数 bool(x) 用x创建一个布尔值(true/false) bool(obj)返回假值的情况:
None 空值
false 假值
0
0.0
0j
所有的数字零
‘’ 空字符串
{} 空列表
[] 空词典
() 空原组
... 函数调用表达式:
函数名(传参列表)
说明:函数调用表达式时,此表达式一定是会返回一个对象的引用关系
如果不需要返回值时,通常返回none对象的引用关系 内建数值型函数:
abs(x) 取x的绝对值 round(number,ndigits=0) 对数值进行四舍五入 ,ndigits是小数向右取整的位数,负数表示像左取整 pow(x,y,z=none) 相当于x**y或x**y%z help()查看帮助 help(函数或对象名) help(int) 语句: 语句是由一些表达式组成,通常一条一句可以独立执行来完成一部分事情并形成结果
Python建议一条语句写在一行内
多条一句子写在一行内需要用“;”分开 [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em] | print("hello")
x = 100 + 200
print(x)
print("hello"); x = 100 + 200; print(x)
|
显示换行:
折行符“\”
折行符必须一行的末尾,来告诉解释执行器下一行也是本行的语句 隐式折行符:
所有的括号的内容换行,成为隐式折行符()、{}、[] 函数的使用:
基本输入函数input
从标准输入设备上读取一个字符串(末尾的换行符会被删除)
返回输入的字符串(仅Python3) 提示字符可以为空 基本输出函数:
print
将一系列的值一字符串的形式输出到标准输出设备上,默认为终端
选项的关键字参数:
sep:两个值之间的分隔符,默认为一个空格
end:输出完毕后在末尾自动加一个字符串,默认为换行符(\n)
练习:
1.输入两个整数,分别用变量x,y绑定
1)打印输出计算这两个数的和
2)打印输出计算这两个数的积
3)打印输出计x的y次方 答案: [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em] | x = int(input("plwase input integer:"))
y = int(input("plwase input integer:"))
print(x + y, "\n", x * y, "\n", x ** y)
|
2.今天是小明的20岁生日,假设每年都有365天,计算他过了多少个星期天,剩余多少天 答案: [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em] | print((20 * 365) // 7, "星期天 剩余", (20 * 365) % 7, "天")
|
3.本别输入当前时间的时、分、秒 在终端打印输出当前距离0:0:0过了多少少天 答案: [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em] | h = int(input("plwase input hour:"))
m = int(input("plwase input minute:"))
s = int(input("plwase input second:"))
print(h * 3600 + m * 60 + s, "second")
|
if语句:
让程序根据条件选着性的执行某条语句或某些语句 语法: [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em] | a = int(input("plaese input integer:"))
if a > 0:
print(a, ">0")
elif a > 6:
print(a, ">6")
elif a > 100:
print(a, ">100")
else:
print(a, "<0")
|
elif可以有0个或多个
else可以有零个或1个 并且所有语句当中只能执行一个 if的嵌套:
if语句本身是由多条子句组成的一条复合语句
if语句可以作为语句嵌套到另一个语句内部 条件表达式:
表达式1 if 真值表达式 else 表达式2
根据真值表达式的取值(true、false)
来决定执行表达式1或2,并返回结果 [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em] | money = int(input("100"))
pay = money - 20 if money >= 100 else money
|
pass语句:
通常用来填充语法空白又名空语句 布尔运算符:
not and or
布尔非 not
如果为true返回false否则为反
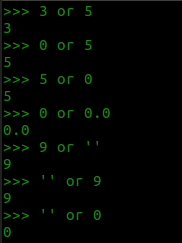
布尔或 or
优先返回真值
见true得true
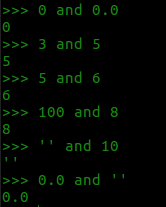
布尔与 and
优先返回假值对象
见false得false
正负号运算符:
+ 表达式
- 表达式
这是一个一元运算符(只有一个数据参加运算)
练习:
1.北京出租车价格 3公里以内13元
基本单价:2.3元/公里(超出3公里以外)
回空费:超过15公里 每公里 加收单价的50%的会空费(3.45元/公里)
输入公里数 打印费用金额 答案: [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| kilometre = int(input("plaese input kilometre:"))
if kilometre < 0:
if kilometre > 15:
money = (kilometre - 15) * 3.45 + (15 - 3) + 13
print("money:", money, "$")
elif 3 < kilometre < 15:
money = (kilometre - 3) * 2.3 + 13
print("money:", money, "$")
else:
print("money:13$")
else:
print("not'is kilonetre")
|
2.输入一个学生的三科成绩(3个整数:
打印出最高分、最低分、平局分是多少
答案: [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| a = int(input("plaese input english mark:"))
b = int(input("plaese input language mark:"))
c = int(input("plaese input mathematisc mark:"))
if 100 > a > 0 and 100 > b > 0 and 100 > c > 0:
if a > b and a > c:
print("top score english:", a)
elif b > c and b > a:
print("top score language:", b)
elif c > a and c > b:
print("top score mathematisc:", c)
if a < b and a < c:
print("lowest english:", a)
elif b < c and b < a:
print("lowest language:", b)
elif c < a and c < b:
print("lowest mathematisc:", c)
print("mean:", (a + b + c)/3)
else:
print("not'is mark")
|
3.bmi指数(body、mass、index)以称身体质量指数
bmi的计算公式: bmi = 体重(公斤)/身高的平方
标准表: bmi< 18.5 体重过轻
18.5<=bmi<24 体重正常
bmi> 24 体重过重
输入公斤体重、身高 打印出 bmi的值 并打印体重状况 答案: [backcolor=rgb(255, 255, 255) !important][size=1em]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| z = int(input("plaese input your weigh:"))
g = float(input("plaese input your height:"))
if z < 0 and g < 0:
bim = (z / g) ** 2
if bim < 18.5:
print("your bim qing")
elif 24 > bim > 18.5:
print("your bim normal")
else:
print("your bim serious")
else:
print("your inuput error")
|
|